Heart Disease
Embryonic stem cell transplantation has a positive and significant effect on improving heart and blood circulation in patients with myocardial infarction, cardiac sclerosis and hypertension. Clinical data shows that embryonic stem cell transplantation has a significant effect on myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease.
After embryonic stem cell transplantation, the patient's symptoms have been improved. These improvements include reduced powerlessness, increased physical fitness, increased appetite. The sleep condition improved; symptoms of depression reduced and thinking and memory enhanced. At the same time, the patients are in high psychological emotion. Blood pressure dropped in 80% of patients. Before transplantation, patients need to take antihypertensive drugs, but within 2-4 weeks after transplantation, 45-50% of patients reduced the amount of antihypertensive drugs and nitrate-containing drugs. Most of the patients found that cholesterol and triglyceride restored to the standard values and the level of lipoprotein decreased. Blood circulation have improved for most patients, thanks to increased prothrombin and prolonged coagulation time.
Repair of Damaged Heart Tissue
Objective:To use stem cells to repair damaged heart tissue during a heart attack.
Efficacy:Stem cells have the ability of cardiac tissue differentiation, which can induce and promote the targeted homing of stem cells to the heart, integrate stem cells into injured myocardium, promote the differentiation of cardiac precursor cells, and thus enhance the potential of cardiac self-repair.
Growth Of Cardiovascular
Objectives:Angiogenesis - the growth of new blood vessels.
Efficacy:Several stem cells from different sources, including dental pulp stem cells, have been shown having the ability to stimulate capillary growth.
Eye Disease

Apart from eye inflammation, ocular muscular atrophy is the most common eye disease. According to the clinical category, muscular atrophy can be divided into two types: early (no medical history) and late (inflammation or injury is the cause of muscular atrophy). Embryonic stem cell transplantation is a good way to improve and inhibit muscular atrophy.
After transplantation of embryonic stem cells, the improvement of eye fibers, the improvement of optic nerve function and the improvement of different retinal disorders were observed (e.g., enzymatic diseases affecting cells, nuclear glycolic acid/tryptophan dysfunction, nerve receptor injury, retinal pigment epithelium tissue and retinal ganglion cell dysfunction).
Corneal Disease
Objective:To improve the visual acuity of patients with keratopathy by using stem cells.
Efficacy:A British study has concluded that limbal stem cell transplantation is a "safe and effective way to reconstruct corneal surface and restore visual acuity".
Macular Disease
Objective:Use stem cells to make specialized cells to help treat Stargardt macular malnutrition and dry macular denaturation.
Efficacy:This test of stem cell therapy for macular disease is in its infancy. Two patients have been reported with no side effects.
Diabetes
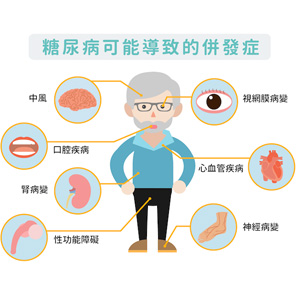
Diabetes-related metabolic disorders cause a large number of complications, including cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, retinopathy, nephropathy and poor wound healing. Stem cells stimulate the formation of new blood vessels and regulate inflammation by releasing soluble growth factors and cytokines, providing a promising method for diabetic complications. In addition, the autologous cell-based approach is an ideal way to minimize immune rejection.
Diabetes
Objective:Use stem cells to fight type 1 diabetes.
Efficacy:After isolating, purifying and amplifying the extracted stem cells in vitro, transfusing them into diabetic patients, the stem cells will differentiate and proliferate into islet cells like seeds under the induction of pancreatic tissue microenvironment, to replace the damaged islet beta cells, secrete insulin, and promote the regeneration and repair of damaged islet cells. So it can play a fundamental role in the treatment of diabetes. A large number of treatment cases show that the use of stem cells after treatment will not produce complications and side effects, and can improve the body's immunity, and even enable patients to get rid of lifelong injection and medication.
Stroke
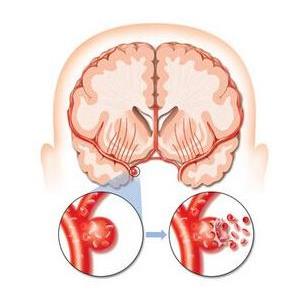
The basic mechanisms involved in stem cell therapy for stroke include anti-apoptosis, anti-inflammation, promoting the regeneration of blood vessels and nerves, forming new nerve cells and neural circuits, antioxidation and protection of blood-brain barrier. Exogenous stem cells and endogenous neural stem cells are commonly used in stroke treatment. Exogenous stem cells include embryonic stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells, neural stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Pre-clinical data shows that cell therapy has great potential to improve stroke treatment. Up to now, 47 clinical studies on stem cell therapy for stroke have been registered at http://clinicaltrials.gov. These clinical studies have shown that stem cells have made important progress in the treatment of stroke.
Stroke
Objective:To use stem cells to offset brain damage caused by stroke, repair the tissue in the damaged area of stroke, and reverse the disability caused by stroke.
Efficacy:Stem cells can make brain work better. Stem cells can differentiate into new nerve cells after transfusion into human body, which can provide a new cell source for the brain, and can effectively improve the condition of brain aging. Especially for the memory and intelligence of senile dementia patients, there is a significant improvement and recovery.
Spinal Cord Injury
Mesenchymal stem cells have entered the clinical stage in the treatment of spinal cord injury. According to the results of investigations on the therapeutic effects of a large number of cases, patients with spinal cord injury could receive mitochondrial stem cells after intervention, and have a certain clinical effect in relieving dyskinesia, sensory disturbances, convulsions and perspiration improvement. Data analysis including exercise score analysis, sensory score analysis, simulated visual score analysis, functional assessment of daily living ability, vital sign observation and laboratory examination at different time points after stem cell treatment all showed a certain degree of improvement.
In 2009, scientists at the University of São Paulo Medical School in Brazil published a study involving 39 patients with chronic spinal cord injury. They infused stem cells into the femoral artery in the patient's leg, and the researchers said the therapy was safe and 26 patients’ stimulation response was improved(66%).
Spinal Cord Injury
Objective:Use stem cells to treat chronic spinal cord injury in patients with varying degrees of paralysis.
Efficacy:Stem cells can differentiate into bone, cartilage, muscle, tendon, ligament, nerve and other tissue cells under the specific induction conditions in vivo or in vitro. As seed cells, they can be used for damage repair of tissues and organs.
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is one of the common neurodegenerative diseases. The main pathogenesis is caused by the progressive loss of dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra. The purpose of treatment is to compensate or replace the lost dopamine. Scientific research has confirmed that stem cells have great potential in the treatment of Parkinson's field. By transplanting stem cells into the patient and replenishing missing or defective nerve cells, it is expected to fundamentally treat Parkinson's disease.
Human embryonic stem cell differentiation derived neural precursor cells can continue to differentiate into dopaminergic neurons in the brain, which can supplement the dopaminergic neurons missing in Parkinson's patients, and can theoretically treat Parkinson's disease. This therapy requires preclinical data to confirm safety and efficacy before entering clinical applications. The newly published new results provide a scientific basis for conducting relevant clinical research. With the further development of clinical treatment, Parkinson's treatment will usher in a new dawn. Chinese scientists have recently revealed in STEM CELLS that stem cell transplantation helps to treat Parkinson's disease by stimulating the production of more nerve cells by subventricular zone (SVZ) stem cells.
Parkinson's Disease
Objective:Use stem cell intervention to treat and control the development of Parkinson's disease and improve the patients’ life quality.
Efficacy:Stem cell transplantation is considered to be a very effective treatment for Parkinson's. Stem cells have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into any type of nerve cell, such as differentiation into neurons and glial cells, with the ability to rescue dysfunctional neural pathways.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (also known as spinal scoliosis) is a disease in which muscles are gradually weakened and atrophied. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis usually dies of respiratory failure within three to five years (rarely to 7 years) and there is no cure. Degeneration of motor neurons that control skeletal muscle in the central nervous system. Symptoms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are atrophy of the hands and feet and respiratory muscles.
Transplantation of embryonic stem cells does not cure amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is still unknown, but transplantation of embryonic stem cells for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis can effectively alleviate the symptoms and slow the rate of deterioration. Transplantation of embryonic stem cells for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis can effectively improve the patient's ability to live and work, and also prolong life.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Objective:Test the safety of stem cells delivered to the spinal cord.
Efficacy:A clinical trial conducted by Eva Feldman of the University of Michigan at Emory University shows that three patients have so far been treated with stem cells without side effects.
Multiple Sclerosis
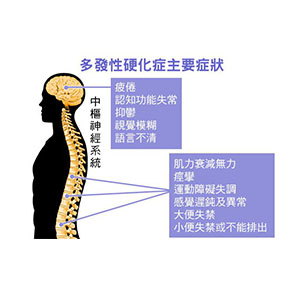
Using fetal stem cells to provide treatment for multiple sclerosis (MS), which has improved most patients’ diseases. The goal of treatment for multiple sclerosis is to stop immune aggression, that is, counter the internal attack on the patient's autonomic nervous system by destroying the primary mechanism of the disease. This can achieve a decline or regression of symptoms of the nervous system.
In the treatment of multiple sclerosis, stem cells have two major effects:
Preventing nerve cell damage: Stem cells can reduce or even prevent damage to nerve cells. This process is called "neurological protection".
Damaged Myelin Repair:The myelin layer that protects nerve fibers is damaged by the autoimmune system of patients with multiple sclerosis. Specialized stem cells in the brain can produce myelin-producing cells, which promote the repair of myelin. This process is called "myelin regeneration".
Multiple Sclerosis
Objective:Use stem cell suppression and then reset the immune system for the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Efficacy:Clinical studies have shown that stem cell therapy has a sustained effect on patients with invasive multiple sclerosis who are ineffective in inhibiting conventional therapy, and can also lead to sustained clinical improvement, especially in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.
Cancer-Glioblastoma
Embryonic stem cell transplantation for the treatment of malignant tumors is not an alternative to conventional treatment options. Stem cell therapy can only be performed after surgery, "classic" chemotherapy or radiation therapy if the doctor determines the treatment plan.
Although the “typical” treatment of cancer is accompanied by side effects, stem cell treatment is to address the following at first: Partial recovery of anti-tumor immunity and hematopoietic function;Improve the quality of life of patients – inability to decline, overall improvement, physical and psychological improvement.
Glioblastoma
Objective:Use stem cells to destroy gliomas.
Efficacy:There is a trial currently: Hope of Hope, a medical center in California, is genetically modifying neural stem cells in order to produce a drug that can convert a non-toxic drug (5-fluorocytosine or 5-FC) into a cancer treatment (5-fluorouracil or 5-FU). The clinician infused the modified stem cells into the patient's brain, hoping that the stem cells can spread to the tumor and lock onto it. When 5-FC reaches the tumor site, the attached stem cells help convert it to the cancer drug 5-FU, with the goal of reducing or destroying glioblastoma while avoiding toxic effects on other parts of the body.
Leukemia And Other Blood Diseases
Leukemia is a type of malignant clonal disease of hematopoietic stem cells. Clonal leukemia cells proliferate and accumulate in bone marrow and other hematopoietic tissues due to uncontrolled proliferation, differentiation, and obstruction, and infiltrate other non-hematopoietic tissues and organs, while inhibiting normal hematopoietic function. Clinically, varying degrees of anemia, hemorrhage, infection, fever, and swelling of the liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone pain can be seen.
In addition to a few special patients may benefit from autologous transplantation, the majority of leukemia patients should be transplanted. With the advancement of transplantation technology, donor selection, transplantation risk and long-term prognosis have made significant progress.Therefore,allogeneic transplantation is an important and radical means of various high-risk leukemia.
Leukemia And Other Blood Diseases
Objective:Improve the body's immunity; enhance disease resistance.
Efficacy:One of the first uses of stem cells is to treat blood and immune disorders. After infusion of stem cells, the hematopoietic immune system can be re-established and normal immune function restored. Today, stem cell transplantation has become a standard treatment in these conditions.
Cartilage Repair
At present, the conventional treatment of knee cartilage wear is analgesic anti-inflammatory drugs, acupuncture, plaster, etc. These treatments cannot prevent the disease from worsening, and it is a last resort to replace the joints with artificial joints. It can eliminate joint discomfort to a large extent, and generally maintains basic motor function for about ten years. However, surgery has a great risk, whose fixation and meshing may not be satisfactory. Postoperative joint function is limited, it is easy to slip off and bruise, and it can not completely eliminate the pain. For the elderly, the physical burden of the operation is especially big. Artificial joints generally have a service life of about 10-15 years, and the joints still need to be replaced at the end of the period, increasing the pain.
Stem cells are the best treatment for effective treatment. After the fat stem cells are returned to the human body, they differentiate into new chondrocytes and osteoblasts, supplement the missing old cartilage and osteoblasts, and effectively activate cartilage and osteoblasts. Self-healing function, repair damaged cartilage and osteoblasts, improve muscle strength, muscle tightness, in order to improve the waist and knee soreness and cure the disease.
Cartilage Repair
Objective:Making use of stem cells to make new cartilage.
Efficacy:Once the bone and joint are damaged, it is difficult to repair, which will lead to irreversible joint degeneration and bone and joint disease. Using stem cells can repair joint damage and improve function. Some clinically have indicated that stem cells have been used to embed gel or collagen sheets and place them in areas of cartilage damage (such as knees or ankles).


SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER